Water Management

Identification of Water Risks and Opportunities
The United Nations Water Resources Organization (UN WATER) released the 2024 UN World Water Development Report, which states that climate change is causing an ongoing water crisis due to frequent record-breaking torrential rains and droughts around the world. Cherishing and making good use of water resources has always been a policy actively promoted by ChipMOS. In 2023-2024, we introduced the ISO 46001 Water Efficiency Management System in our major water-consuming plants (Zhubei fab. and Tainan fab.) to establish baseline data for water consumption, set water-saving goals, and implement water-saving plans through systematic management, thereby enhancing corporate water efficiency and identifying risks and opportunities related to water resources.
In 2024, members of the ChipMOS Sustainability Committee collectively reviewed and discussed our water-related risks and opportunities. Recognizing that water-related issues have remained relatively stable in recent years, we maintained the same assessment results as our 2021 identification. We plan to enhance our review of water resource scenario analysis in 2025.There are a total of 70 items of risks and opportunities: 51 water risk items, with two being major; nine medium water risks; 19 water opportunity items, with three being major; and two medium water opportunities.
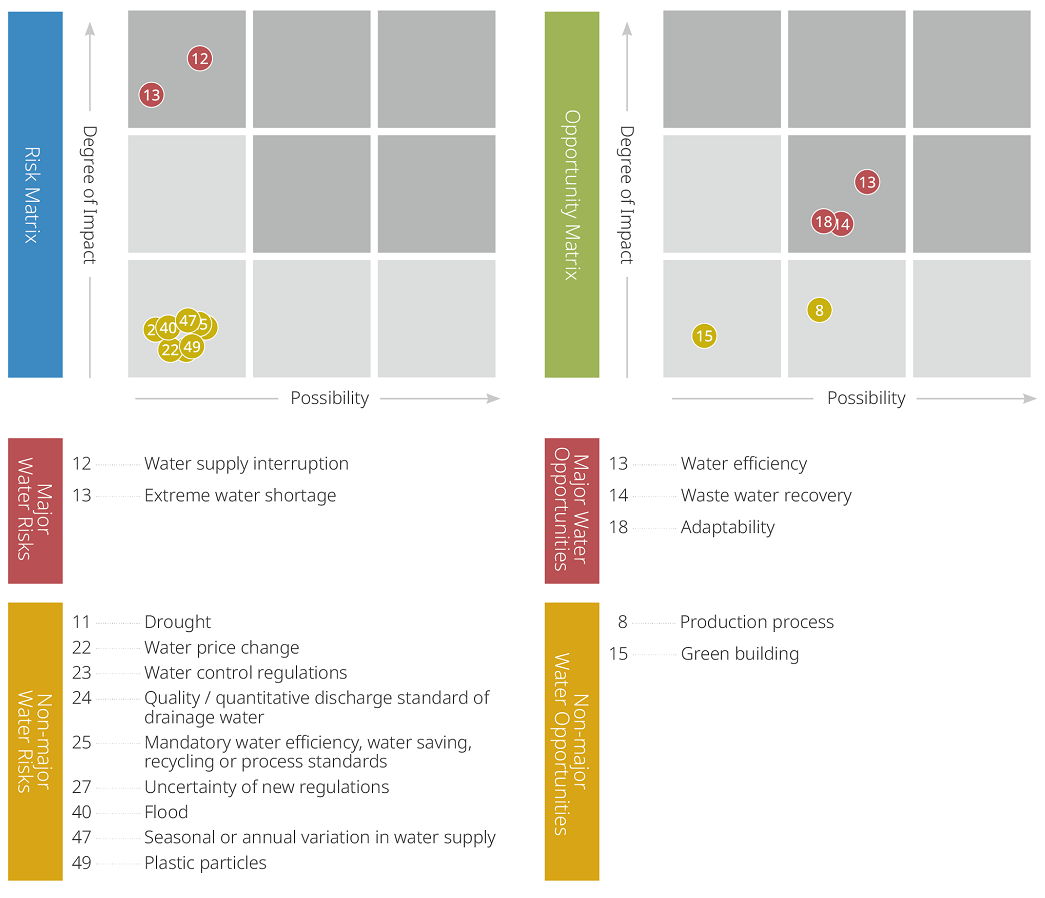
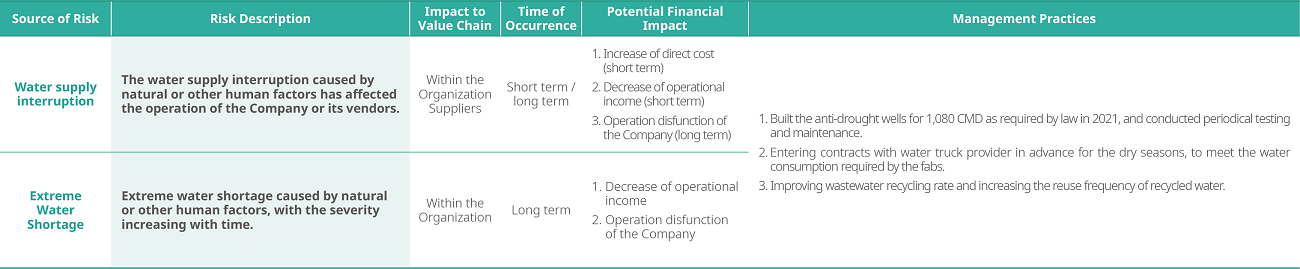
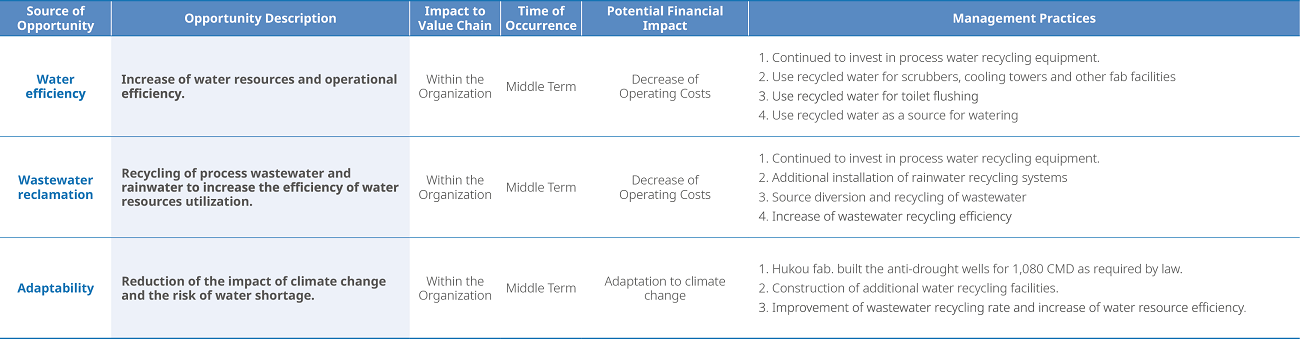
Water Resources Risk Management
ChipMOS actively implements the ISO 46001 water efficiency management system to establish systematic data on the change of water flow and water volume. and use big data to analyze possible water risks within the fab. The Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas of the World Resources Institute (WRI) is used to identify the risk level of water supply in the area where the fab is located; through the analysis of internal and external information, it is more helpful for ChipMOS to perform Risk management of water resources. Currently, all fabs of ChipMOS are in the low or mid-low area of water resource pressure. However, in response to the risks gradually brought about by climate change, we still adopt enhancement of water saving as our main water use strategy. According to the data of water resources access sources and total water intake, the water impact of the Tainan fab. came to 0.181%, which is relatively higher compared to other facilities in terms of the impact on water source areas. This is primarily due to the larger water demand resulting from the packaging process characterized by the fab’s products.
Introduced ISO 46001
In 2023, ChipMOS Zhubei and Tainan plants introduced the ISO 46001 Water Efficiency Management System, which systematically surveyed water usage conditions, identified major water-consuming equipment, established performance indicators and baselines, explored potential water-saving measures, and implemented feasible water-saving measures and improvement strategies. The water management plan includes continuously setting up rainwater recycling systems and improving wastewater diversion pipelines to enhance recycling and reuse, striving for maximum water efficiency.
Note: Considering the production process characteristics of the products, Zhubei fab. and the Tainan fab. have high water demand and complex processes, so the implementation of the ISO 46001 management system is prioritized.
In 2024, ChipMOS will continue to implement various water-saving measures, with the main water-consuming plants in Zhubei and Tainan as key implementation points, improving water resource utilization efficiency through advanced water management and big data analysis of water consumption; the water recycling rate at the Zhubei plant increased from 65.2% to 66.85%, exceeding the 2024 water target; the manufacturing process water recycling rate in Tainan reached 86.05% in 2024, surpassing the preset target (>85%), and the overall water recycling rate for all plants also reached 85.14%, exceeding the preset target (>80%).
Recycling of Process Water
Water resource management not only involves conserving water but also creating new sources of water. At ChipMOS, our main focus is on increasing the efficiency of recycling process water in areas with high water consumption, such as the Tainan plant. Since 2008, we have invested in building grinding and cutting process water recycling equipment, using UF membrane systems that utilize pressure as a driving force for membrane separation to recycle process water. In 2023, we installed process water recycling equipment at our main water-consuming facility in northern Taiwan, the Zhubei plant. As of 2024, the cumulative amount of recycled water is 324 million liters. The total amount of process water recycled across all facilities in 2024 was 1,352 million liters, and over the past 17 years, we have saved a cumulative total of 13,899 million liters of water, equivalent to nearly 5,560 international standard swimming pools.
Wastewater Treatment and Discharge
Wastewater treatment and discharge are the final link in water resource management, having the most direct impact on the environment. Therefore, ChipMOS carefully carries out wastewater operations through 24-hour monitoring equipment, self-water quality inspection, and personnel environmental education training to ensure that the management process and discharged water quality comply with relevant regulations. By utilizing baseline data and water quality stratification, different types of wastewater are identified for appropriate treatment, achieving the goals of reducing wastewater, increasing recycling, and harmless discharge.
ChipMOS Hsinchu, Zhubei fab. 2, and Hukou fab. have no process wastewater. The Hsinchu plant and Tainan plant are located in the science park, while the Hukou plant is located in an industrial zone. They all pass through the sewage treatment plants of the science park or industrial zone for unified treatment before being discharged into a receiving water body approved by the environmental protection agency. The Zhubei plant also undergoes wastewater treatment and meets the discharge standards before discharging into an environmentally-approved receiving water body.
Water Management Precautionary Alerts and Contingency Actions
With reference to the data of the AQUEDUCT Water Risk Atlas data of the World Resources Institute (WRI), we identify the water stress of ChipMOS' main fabs (Hsinchu and Tainan) as medium to low risk level. Considering the risk of extreme climate change, we use digitized real-time information of water conditions to monitor the water supply situation 24 hours a day, track and observe the reservoir water storage capacity for each fab, and keep abreast of water conditions with reference to the relevant meteorological information of the Central Weather Administration. In addition to the early source water waring, we monitor the water supply equipment of each fab in a real-time manner. If the water storage volume of the tap water tank falls below the warning value, we immediately make sure whether the source water and water supply equipment are normal to facilitate subsequent response measures.
In response to the water shortage crisis, the Company has implemented three major contingency measures

ISO 14046 Water Footprint
About water resources management, in addition to saving water and recycling water, we also improve the water resource efficiency of the supply chain through the water footprint check mechanism. Moreover, we conduct a check in accordance with ISO 14046 and undergo third-party verification, in order to improve the reliability of data. Since 2014, ChipMOS has completed the ISO 14046 water footprint verification of its products, and has passed the third-party certification, so as to effectively master the water resource status of production and provide customers with reference. The products that completed their check include: LCD Driver IC (bare crystal flip chip), LCD driver IC (COF), 8 "and 12" au bumped wafer, ball grid array package (BGA), quad flat non-lead package (QFN), etc.